“`html
Smart Guide to Calculating the Area of a Pyramid
Understanding the area of a pyramid is crucial for students and professionals alike, ranging from academic settings to practical applications in architecture and design. In this guide, we’ll delve into the necessary formulas, dimensions, and methodologies to calculate not only the area but also the volume of various types of pyramids. Whether you’re dealing with a triangular pyramid, a square pyramid, or a rectangular pyramid, this comprehensive overview will equip you with foundational knowledge and practical insights.
Pyramid Formula Fundamentals
The foundation of calculating the area and volume of pyramids relies on understanding a few key formulas. The essential formula for the surface area of a pyramid is a combination of the area of its base and its lateral area. For example, if you’re working with a square pyramid, you’ll calculate the area of the base using the formula:
Base Area = Base Edge Length²
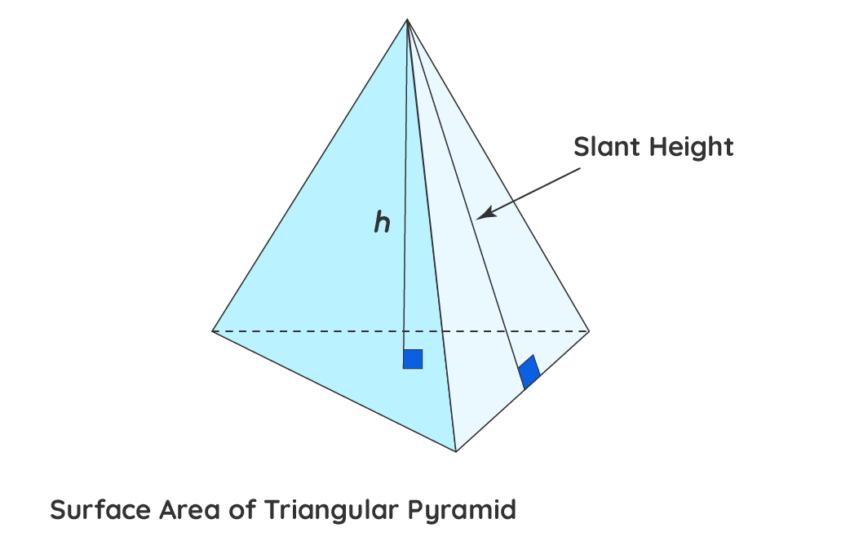
The lateral area of the pyramid, which is crucial for understanding its structure and aesthetics, can be calculated separately. This relies on determining the slant height—an important dimension in the geometry of pyramids—understanding that:
Lateral Area = 1/2 × Perimeter of Base × Slant Height
By combining these calculations, you can derive the total surface area. Applying these formulas allows for critical insights into the spatial configuration of building designs, vital for architects and engineers focusing on pyramid construction.
Understanding Pyramid Height and Its Measurements
When considering the height of a pyramid, it’s vital to distinguish this from the slant height. The vertical height, or perpendicular height, can be defined as the distance from the apex of the pyramid to the center of the base. This measurement is essential when calculating the volume using:
Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height
Precisely measuring the height can be challenging in real-world applications, hence employing accurate tools and techniques is critical. In architecture, miscalculation can lead to fundamental errors in structural integrity, affecting the stability of pyramids. Thus, utilizing CAD modeling and other geometry software can significantly improve measurement accuracy.
Pyramid Dimensions and Their Impact
Pyramid dimensions, including the base dimensions and height measurements, significantly influence not only the area calculations but also the overall design. For instance, altering the base edge length affects the base area and, consequently, the entire volume. When changing these dimensions, one should also consider the effects on the shape’s aesthetic and functional properties.
Pyramid dimensions deeply interrelate with properties like stability and spatial reasoning. Additionally, determining the apex angle gives insight into the geometric relationships that exist between a pyramid’s height and its base dimensions.
Applying the Pyramid Surface Area Formula
The pyramid surface area formula involves integrating various geometric calculations and visualizing pyramids in 3D models. For practical applications, calculating lateral surface areas becomes crucial in contexts like architectural design and construction techniques. The adjustments made to create forms that can withstand various loads often rely heavily on these calculations.
Calculating the Total Surface Area
To calculate the total surface area \( A \) of a pyramid, you need to sum the area of the base with the lateral area. Here’s the complete formula depending on the geometric shape of the base:
Total Surface Area = Base Area + Lateral Area
For example, in a square pyramid with a base edge of length b and a slant height s, the total surface area can be determined as follows:
Total Surface Area = b² + (1/2) × 4b × s
In practical scenarios, modifications might be executed to enhance structural integrity or design. Each of these design choices underscores the versatility inherent in pyramidal structures.
Real-World Applications of Pyramid Calculations
The applications of pyramids extend beyond academic explorations into various industrial fields, particularly in engineering and architectural analysis. Understanding the mechanics behind the area calculations enables professionals to craft designs that prioritize strength and stability. A structural engineer may incorporate geometric principles to create buildings, bridges, or even sculptures that mimic the structural integrity observed in natural pyramid forms.
Moreover, educational resources demonstrating these principles help students interactively explore mathematical principles while fostering comprehension and critical thinking about spatial relationships. Incorporating real-life scenarios into mathematical exercises can demystify complex equations, creativity inspiring architectural designs that endure through time.
Pyramidal Structures in Educational Resources
Pyramids serve as an exceptional subject for educational guides in mathematics. Not only do they provide a basis for understanding solids and their properties, but they also foster engagement between educators and students. Geometry concepts like area, volume measurements, and relationships can be visualized effectively through interactive geometry tools or pyramidal activities in classes.
Utilizing Geometry in Architectural Design
Architectural design often incorporates geometric shapes, with pyramids exemplifying principles of structural integrity. Designers frequently turn to pyramids in constructing elements such as roofs, which distribute weight evenly, thanks to their angular characteristics. Engaging students with practical, hands-on methods for exploring pyramids supports a greater understanding of both geometrical principles and their real-world applications.
Interactive Learning and Mathematical Exercises
Using geometric practices in teaching geometry, learners can engage with math concepts in an interactive manner, solidifying their understanding of structural relationships. For instance, activities that involve drawing or modeling pyramids can stimulate thinking about practical math, height adjustments, and volume comparisons among solids like spheres and cubes. These hands-on experiences enrich students’ geometric exploration beyond traditional learning methods.
Key Takeaways
- The area of a pyramid is a critical concept integrating various dimensions and geometric relationships.
- Understanding measurements, especially the pyramid’s height and slant height, is vital for calculating accurate areas and volumes.
- Field applications in architecture and engineering demonstrate the importance of pyramids in real-world design and structural integrity.
- Educational resources and interactive geometry help build foundational knowledge in understanding pyramids and their functions.
- Using modern tools enhances our ability to visualize and apply pyramid calculations in diverse fields.
FAQ
1. What are the primary measurements needed to calculate the area of a pyramid?
To accurately determine the area of a pyramid, you’ll need the base dimensions, height measurements, and slant height, as these elements factor into major calculations including lateral area and total surface area.
2. How do I calculate the volume of a pyramid?
The volume of a pyramid can be calculated using the formula: Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height. This allows you to understand the space the pyramid occupies, which is critical in both academic and real-world applications.
3. Why is the slant height important in pyramid calculations?
The slant height of a pyramid directly impacts the calculation of the lateral area, and it’s essential in determining the total surface area, contributing significantly to the structural stability and aesthetic of pyramid designs.
4. How is the area of different types of pyramids calculated?
The area calculations vary based on the pyramid’s base. For example, the area of a triangular base pyramid requires calculating the base area using the formula Base Area = 1/2 × Base Length × Height of Triangle, followed by calculating the lateral area separately based on the slant height.
5. Can pyramids be used in practical applications like architecture?
Yes, pyramids are utilized extensively in architecture; their geometric properties provide structural stability, making them ideal for roofs and other weight-bearing structures that inherently require durability and strength.
“`